Hello there! So, you wanna know about the secondary market huh? Developed an interest in investing and real estate?
Do you plan on joining the stock market and boost your cash and financial assets? Become a selling investor?
We hear ya! We got definitions, types, examples, and everything there is to know! BUT FIRST…
What Is a Secondary Market?
This is the market where the trading of securities is done. The secondary marketplace consists of both equity securities as well as debt securities.
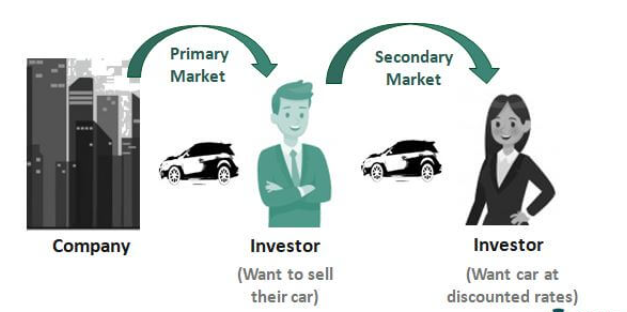
A secondary market is a platform where the shares of companies are publicly traded among investors. It means that investors can freely buy and sell shares WITHOUT the intervention of issuing companies.
Put simply, the secondary market is a place where investors sell and buy securities from other investors that already own the stock.
Say you wanted to buy a Samsung stock. Secondary market means you’d buy from someone who already owns a Samsung stock. Furthermore, Samsung won’t be involved in this transaction.
Here are additional notes:
- In these transactions among most investors, the issuing company does not participate in income generation, and the share value is rather based on its performance in the market.
- Examples of secondary markets are the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. Secondary markets are public markets for shareholders and outside investors to buy and sell secondary shares.
- The cash received for security in the secondary market is income for the investor who is selling the securities.
Secondary Market in Real Estate
The secondary market in real estate is where lenders and investors buy and sell existing mortgages or mortgage-backed securities.
This frees up money for additional mortgage lending. So, you can think of the secondary market as the “resale marketplace” of loans.
Secondary markets are also important for financing real estate purchases. When an investor or buyer purchases a home, the mortgage lender creates loans. This loan origination is the primary market transaction.
They are packaged into mortgage-backed securities and sold to other investors such as pension funds, insurance companies, mutual funds, and hedge funds.
For further example, bonds on secondary markets are sold to investment banks, corporations, and individual investors.
Entities such as Fannie Mae also purchase mortgages on a secondary market. For example, a financial institution writes a mortgage for a consumer, creating mortgage security.
Who Is Fannie Mae?
The real question is, WHAT. It’s known officially as the Federal National Mortgage Association (FNMA).
It’s a government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) chartered by Congress to stimulate homeownership and provide liquidity to the mortgage market.
As a secondary mortgage market participant, It does NOT originate mortgage loans. Instead, it keeps funds flowing to lenders by purchasing or guaranteeing mortgages issued by credit unions, banks, and other financial institutions.
FNMA creates more liquidity for lenders, including thrift and credit unions, which then allows them to underwrite or fund more mortgages. It is one of two large purchasers of mortgages in the secondary market.
Types of Secondary Market
Secondary markets have primarily two types which are the stock exchanges and OTC (Over-the-Counter) markets but there are still other two types that we will mention.
Stock Exchange Market
source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
These are centralized platforms where securities trading takes place between several buyers and sellers. Examples are the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, NSE, BSE, LSE, NYSE, etc.
The investors buy and sell stocks with no direct contact between them. Buys and sells are conducted also through the exchange. There is no counterparty risk, hence the exchange is the guarantor.
Transaction exchanges in new stocks are subjected to stringent regulations in securities trading.
Over-the-Counter Market
OTC markets retain higher counterparty risks in the absence of regulatory oversight, with the parties directly dealing with each other.
Since it is decentralized, there is competition between providers to gain a higher trading volume for their company.
The best price may not be offered by every seller in an OTC market because prices for the securities vary from company to company.
Apart from the stock exchange and OTC market, other types of secondary markets include auction markets and dealer markets.
What Is a Primary Market?
What is a primary market and how is it different from secondary markets? How do the primary and secondary markets function in the stock market?
One of the most common secondary stock markets involves private company shareholders selling equity to outside investors before the company going public. Companies sell new stocks and bonds to investors for the first time.
A primary market is a source of new securities. Often on a trade, it’s where companies, governments, and other groups go to obtain financing through debt-based or equity-based securities.
When a company issues stocks or bond markets for the first time and sells those securities directly to investors, that transaction occurs on primary markets.
During an initial public offering (IPO), a primary market transaction occurs between the purchasing investor and the investment bank underwriting the IPO.
Any proceeds from the sale of shares of stock on the primary market go to the company that issued the stock, after accounting for the bank’s administrative price.
Primary Markets in Real Estate
Real estate primary sales mean when a real estate builder sells the housing units or commercial units to the investor or end-user in the primary market.
In other words, the primary market is where something is sold for the first time.
Primary markets in real estate are where stocks and bonds are also publicly traded for the first time. Sales on the primary market coincide with fixed prices.
Sales in the secondary market fluctuate based on value. Shares can’t trade on the secondary market until they have been issued on the primary market first.
Primary Markets Vs. Secondary Markets
When buying stocks on primary markets, they’re purchased directly from the issuer. With secondary markets, the issuing companies don’t play a part.
Remember our Samsung example in the first section?
This is what you might automatically think of when you think of stock trading. Following an IPO, investors can buy or sell securities and company shares on an exchange.
Now, let’s say some of the investors who bought some of the government’s bonds or bills at these auctions. They’re usually institutional investors, like brokerages, pension funds, or investment funds who want to sell them.
They offer them on stock exchanges or over-the-counter (OTC), where other investors can buy or share prices. These U.S. Treasuries now market the secondary.
The key takeaways between them are the ones who sell securities and the source of securities. In primary real estate markets, it’s the issuer of the shares or bonds or whatever the asset is.
Significance of Secondary Markets
The price and demand of financial markets is one thing, but in real estate, it’s a different story. Here are some benefits to secondary markets in real estate:
- A large majority of home sales are actually resales. Without secondary markets it would be difficult for real estate professionals to make a living out of the real estate business.
- Mortgage-backed securities help investors receive income. Without these MBSes markets initially created, buyers would have a hard time finding financing options. You can see why the demand for these can be high too. To learn more about MBSes, this video should help.
Investing Tips for Beginners
We want to give you a few tips in case you start your journey in investing, make sure you become a wise buyer, trader, and seller!
Know Your Goals and Timeline
Before you start investing, you need to know why you’re investing. Different goals necessitate different strategies.
Your timeline also plays a significant role in your investment strategy. If you’re a young professional, you can handle the volatility that comes with investing in high-risk, high-reward stocks.
Invest Logically, Not Emotionally
Whether you choose to put money on your own or to let a mutual fund or manage your investments, do not let your emotions get in the way.
It can be easy to let your emotions and sentimental attachments to certain companies or brands make you want to buy their shares.
Liking a company isn’t the best reason to buy its assets. You should base your investments on a sound strategy and research.
Price doesn’t always dictate value.
Summing It Up!
Investors buy and trade their properties on the secondary market. Mortgage loans, shares, investment notes, and stock exchange are financial instruments that market the secondary real estate.
We hope this guide helped!